- Home
- Soils in Scotland
-
Maps
-
- Soil maps
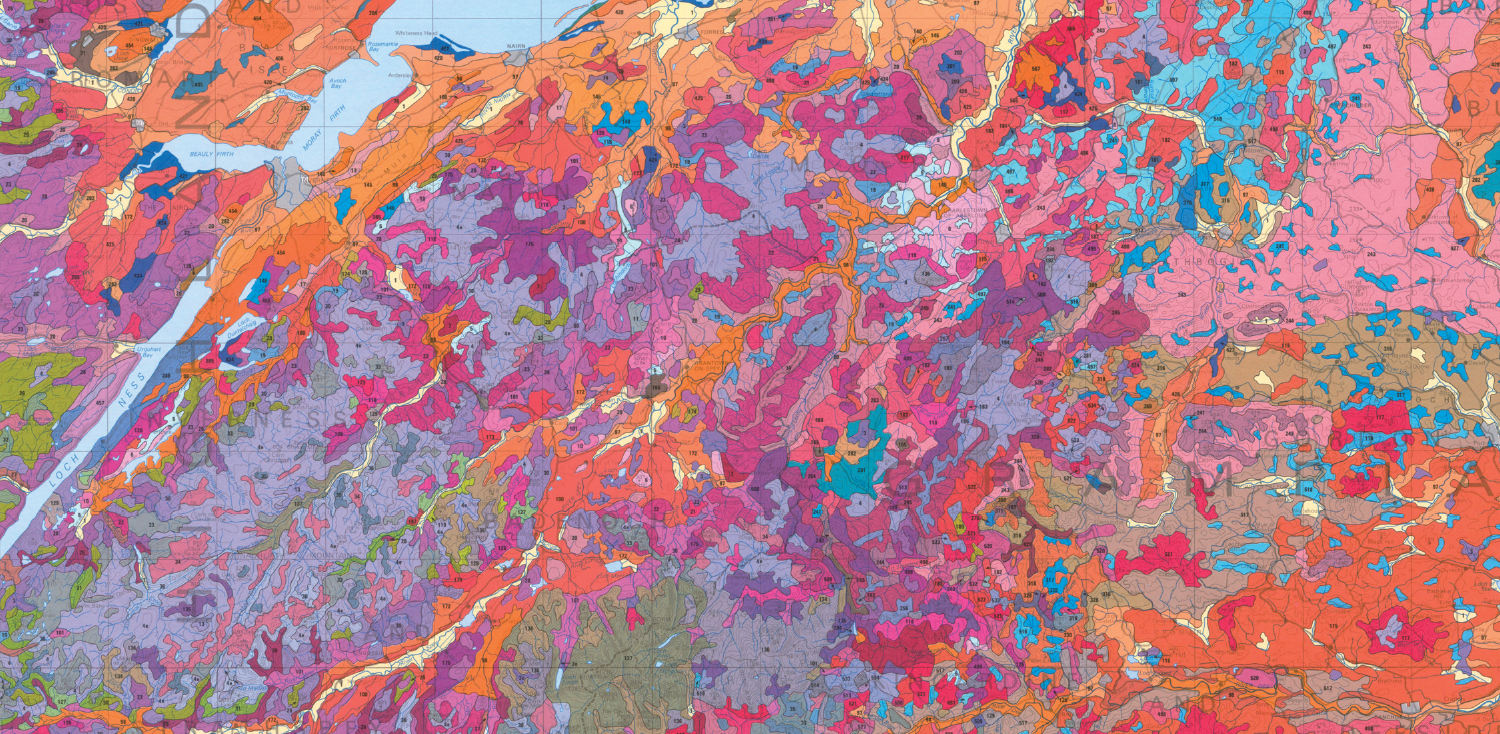
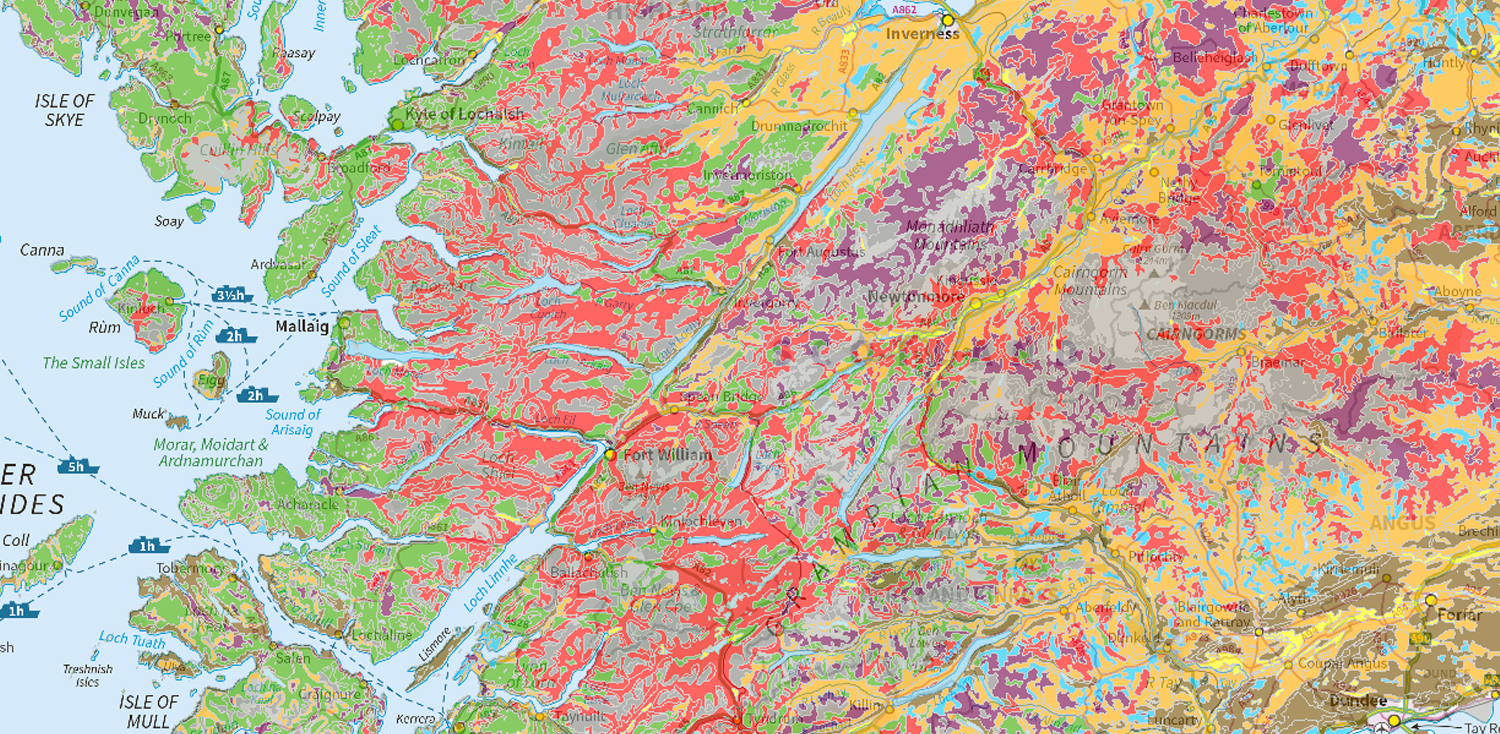
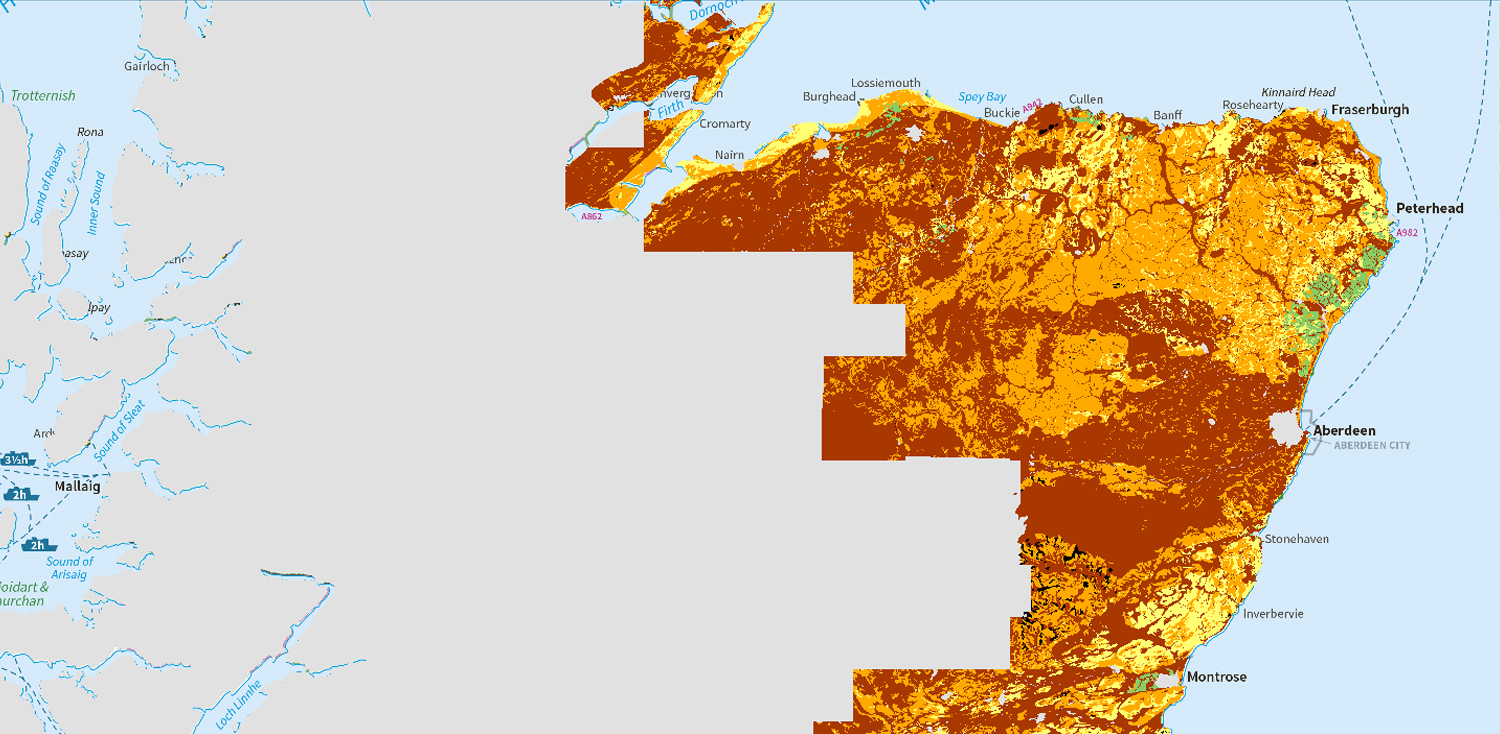
- National soil map of Scotland
- Soil map of Scotland (partial cover)
- World Reference Base soil map
- Scanned soil maps
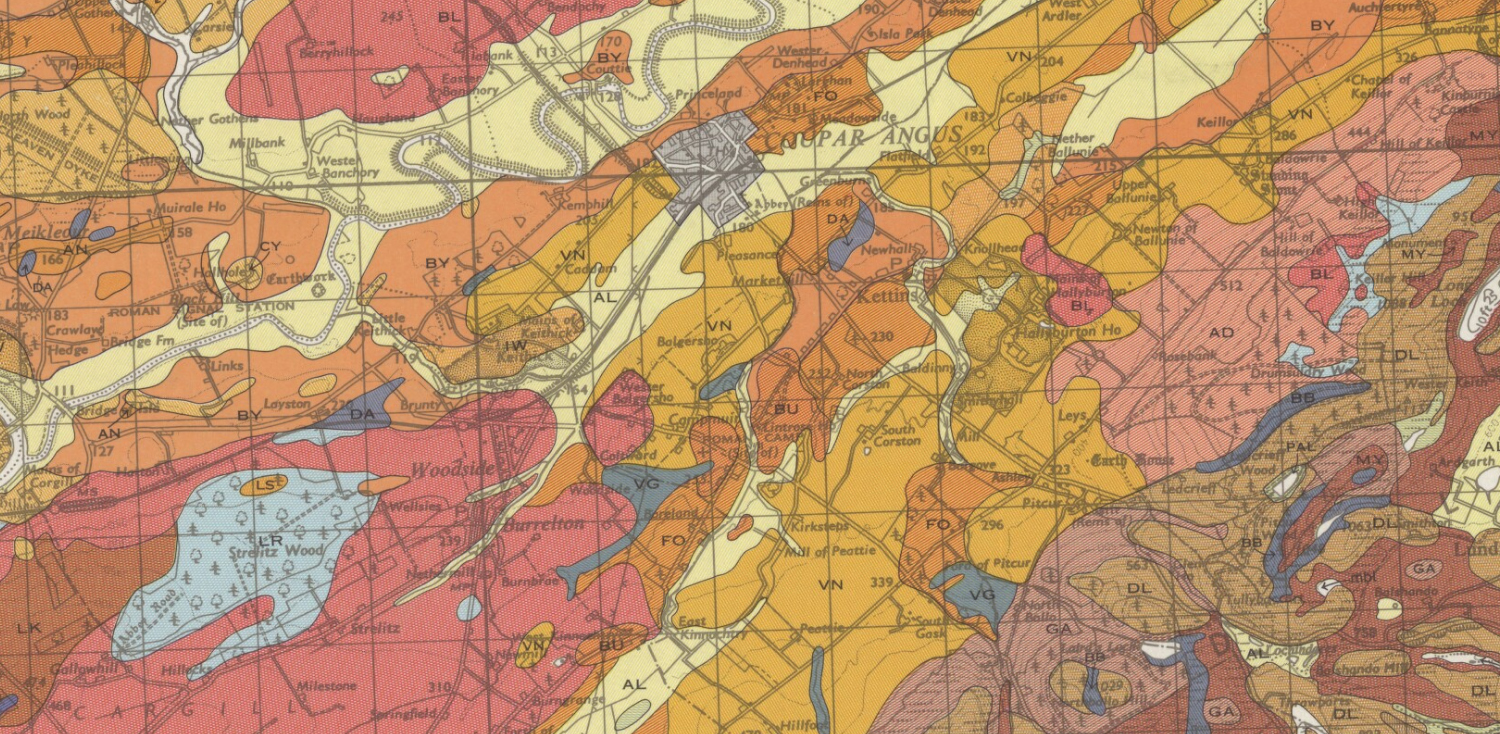
- Soil Survey of Scotland 1:250 000 scanned maps
- Soil Survey of Scotland 1:63 360 scanned maps
- Capability maps
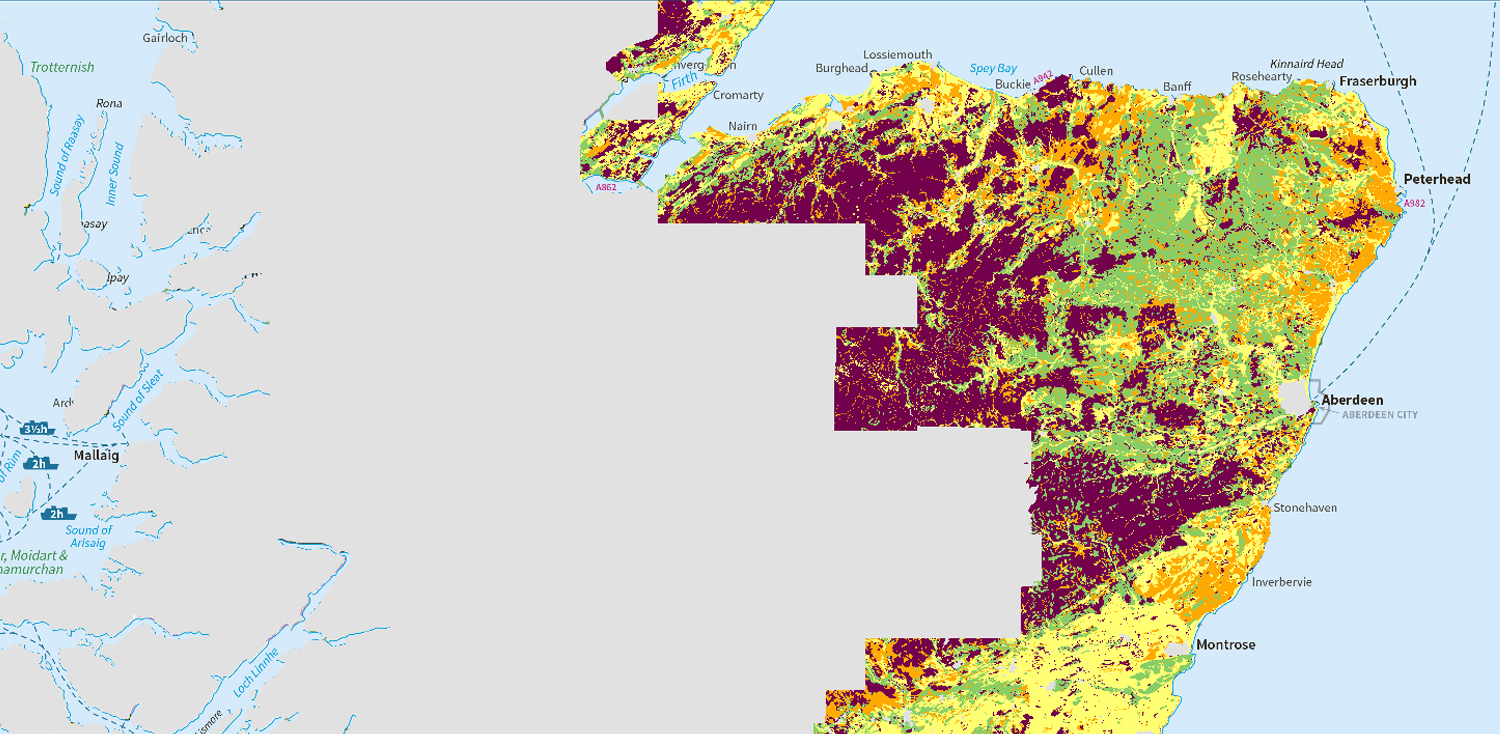
- National scale land capability for forestry
- National scale land capability for agriculture
- Land capability for agriculture (partial cover)
- Thematic maps
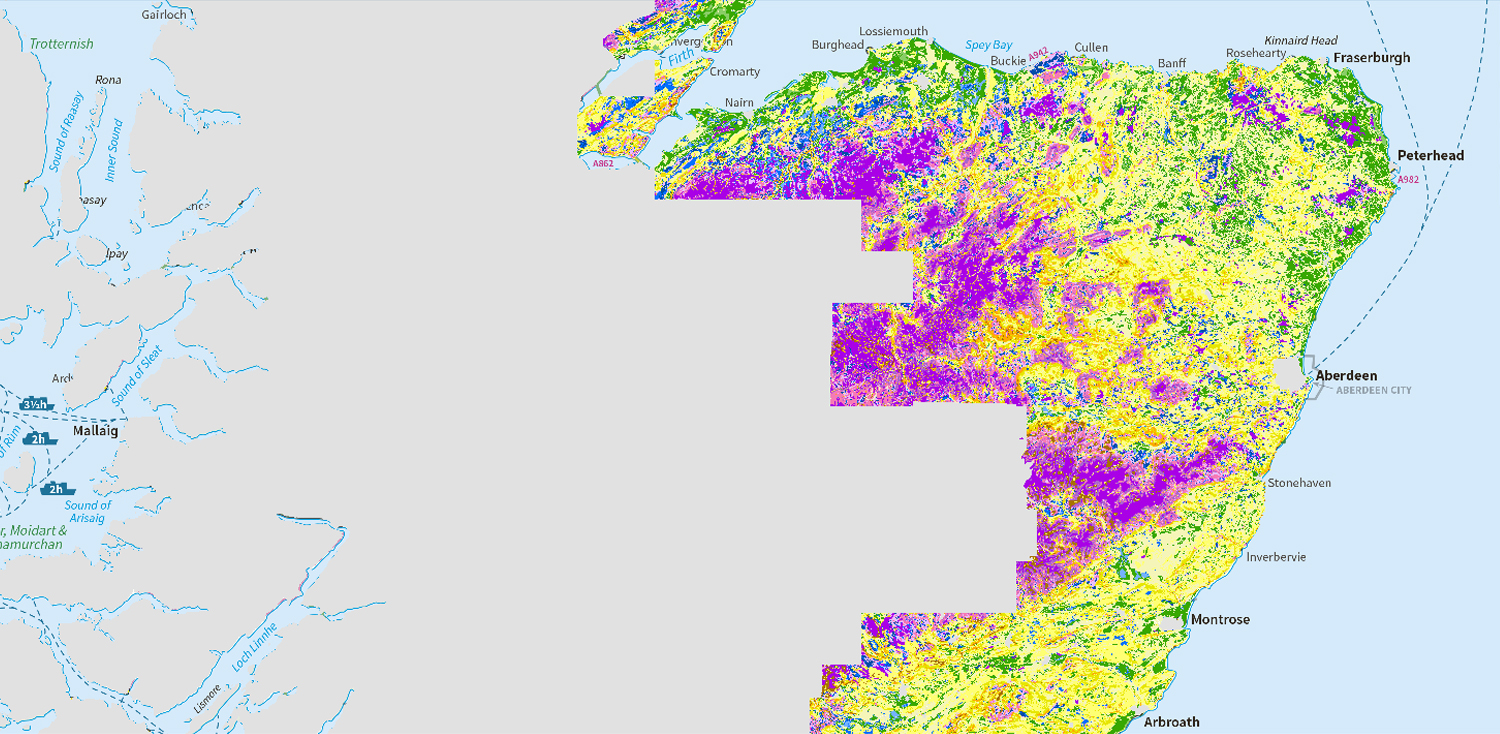
- Map of topsoil organic carbon concentration
- Map of available water capacity
- Map of soil texture in Nitrate Vulnerable Zones
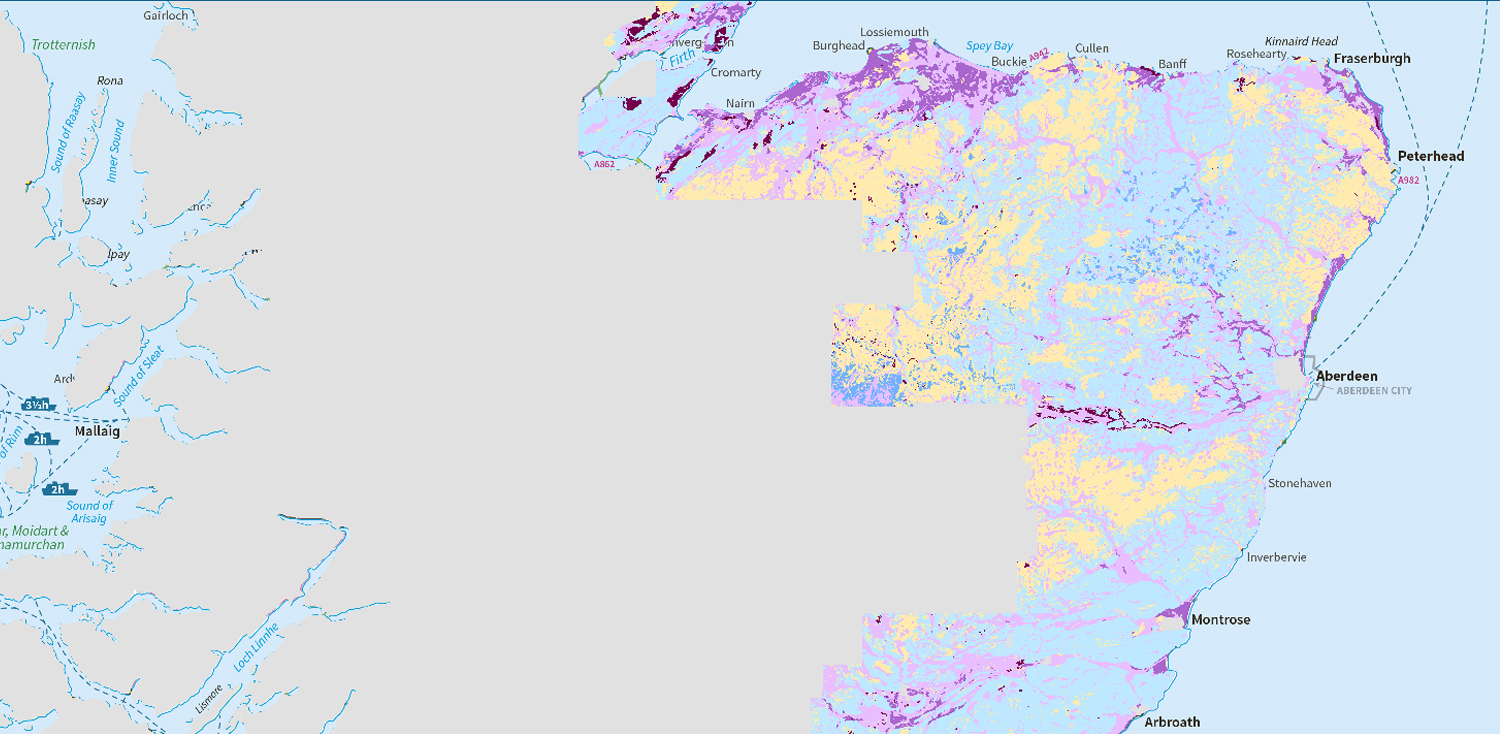
- Carbon and peatland 2016 map
- Map of soil phosphorus sorption capacity
- Resources
- About us
- News